Android Sdk Cryptographic Key Generation
Generate a new secret key. To generate the key, follow the same process as the one for generating a new private key. You use the Security library in each case. Import encrypted keys more securely. Android 9 (API level 28) and higher allow you to import encrypted keys securely into the Keystore using an ASN.1‑encoded key format. This passphrase could be fed into PBKDF2 to generate the encryption key. (PBKDF2 is a commonly used algorithm for deriving key material from a passphrase, using a technique known as 'key stretching'.) Android provides an implementation of this algorithm inside SecretKeyFactory as PBKDF2WithHmacSHA1. Apr 27, 2009 The CNG SDK contains documentation, code, and tools designed to help you develop cryptographic applications and libraries targeting the Windows Vista SP1, Windows Server 2008 R2, and Windows 7 Operating Systems. The Android SDK contains several tools to help you test and debug your Android applications. For more information, see the Debugging and Testing sections in the Dev Guide. Gathering materials and resources. To begin preparing your application for release you need to gather several supporting items.
- Android Sdk Cryptographic Key Generation 1
- Android Sdk Cryptographic Key Generation 2
- Android Sdk Cryptographic Key Generation 2
Key Generation. Before we jump into encrypting your data, it’s important to understand how your encryption keys will be kept safe. Jetpack Security uses a master key, which encrypts all subkeys that are used for each cryptographic operation. JetSec provides a recommended default master key in the MasterKeys class. RandomKeygen is a free mobile-friendly tool that offers randomly generated keys and passwords you can use to secure any application, service or device. KEY RandomKeygen - The Secure Password & Keygen Generator. The build process is similar to the debug build process and can be done using JDK and Android SDK tools. The testing tasks serve as a final check, ensuring that your application performs as expected under real-world conditions. Preparing for release is a required development task and is the first step in the. Cryptographic keys.
-->Creating and managing keys is an important part of the cryptographic process. Symmetric algorithms require the creation of a key and an initialization vector (IV). The key must be kept secret from anyone who should not decrypt your data. The IV does not have to be secret, but should be changed for each session. Asymmetric algorithms require the creation of a public key and a private key. The public key can be made public to anyone, while the private key must known only by the party who will decrypt the data encrypted with the public key. This section describes how to generate and manage keys for both symmetric and asymmetric algorithms.
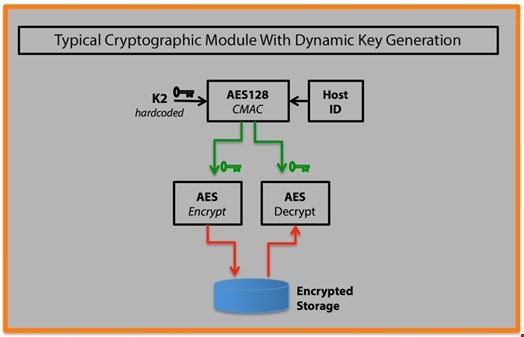
Symmetric Keys
The symmetric encryption classes supplied by the .NET Framework require a key and a new initialization vector (IV) to encrypt and decrypt data. Whenever you create a new instance of one of the managed symmetric cryptographic classes using the parameterless constructor, a new key and IV are automatically created. Anyone that you allow to decrypt your data must possess the same key and IV and use the same algorithm. Generally, a new key and IV should be created for every session, and neither the key nor IV should be stored for use in a later session.
To communicate a symmetric key and IV to a remote party, you would usually encrypt the symmetric key by using asymmetric encryption. Sending the key across an insecure network without encrypting it is unsafe, because anyone who intercepts the key and IV can then decrypt your data. For more information about exchanging data by using encryption, see Creating a Cryptographic Scheme.
The following example shows the creation of a new instance of the TripleDESCryptoServiceProvider class that implements the TripleDES algorithm.
When the previous code is executed, a new key and IV are generated and placed in the Key and IV properties, respectively.
Sometimes you might need to generate multiple keys. In this situation, you can create a new instance of a class that implements a symmetric algorithm and then create a new key and IV by calling the GenerateKey and GenerateIV methods. The following code example illustrates how to create new keys and IVs after a new instance of the symmetric cryptographic class has been made.
When the previous code is executed, a key and IV are generated when the new instance of TripleDESCryptoServiceProvider is made. Another key and IV are created when the GenerateKey and GenerateIV methods are called.
Asymmetric Keys
The .NET Framework provides the RSACryptoServiceProvider and DSACryptoServiceProvider classes for asymmetric encryption. These classes create a public/private key pair when you use the parameterless constructor to create a new instance. Asymmetric keys can be either stored for use in multiple sessions or generated for one session only. While the public key can be made generally available, the private key should be closely guarded.
A public/private key pair is generated whenever a new instance of an asymmetric algorithm class is created. Windows 7 home premium product key generator download. After a new instance of the class is created, the key information can be extracted using one of two methods: download outlook for free mac
The ToXmlString method, which returns an XML representation of the key information.
The ExportParameters method, which returns an RSAParameters structure that holds the key information.
Android Sdk Cryptographic Key Generation 1
Both methods accept a Boolean value that indicates whether to return only the public key information or to return both the public-key and the private-key information. An RSACryptoServiceProvider class can be initialized to the value of an RSAParameters structure by using the ImportParameters method.
Asymmetric private keys should never be stored verbatim or in plain text on the local computer. If you need to store a private key, you should use a key container. For more on how to store a private key in a key container, see How to: Store Asymmetric Keys in a Key Container.
Android Sdk Cryptographic Key Generation 2
The following code example creates a new instance of the RSACryptoServiceProvider class, creating a public/private key pair, and saves the public key information to an RSAParameters structure.