Des Key Generation 56 Bits
Jul 05, 2010 The Data Encryption Standard (DES) is a block cipher (a form of shared secret encryption) that was selected by the National Bureau of Standards as an official Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS) for the United States in 1976 and which has subsequently enjoyed widespread use internationally. It is based on a symmetric-key algorithm that uses a 56-bit key. DES is therefore a symmetric, 64 bit block cipher as it uses the same key for both encryption and decryption and only operates on 64 bit blocks of data at a time5 (be they plaintext or ciphertext). The key size used is 56 bits, however a 64 bit (or eight-byte) key is actually input. From Wikipedia: The key ostensibly consists of 64 bits; however, only 56 of these are actually used by the algorithm. Eight bits are used solely for checking parity, and are thereafter discarded. Hence the effective key length is 56 bits, and it is never quoted as such.
- Cryptography Tutorial
- Cryptography Useful Resources
- Selected Reading
The Data Encryption Standard (DES) is a symmetric-key block cipher published by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).
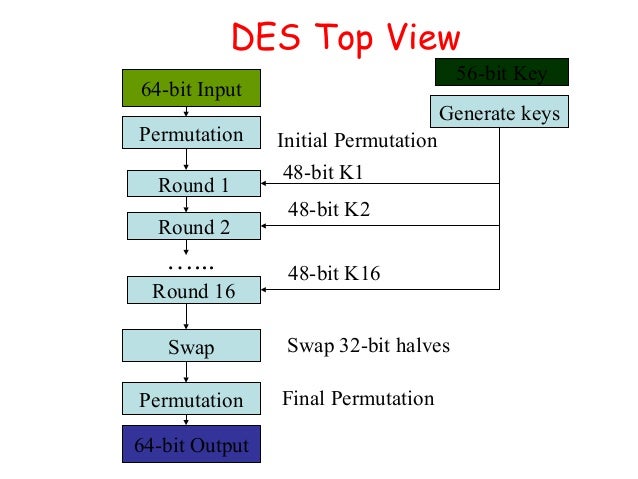
DES is an implementation of a Feistel Cipher. It uses 16 round Feistel structure. The block size is 64-bit. Though, key length is 64-bit, DES has an effective key length of 56 bits, since 8 of the 64 bits of the key are not used by the encryption algorithm (function as check bits only). General Structure of DES is depicted in the following illustration −
Since DES is based on the Feistel Cipher, all that is required to specify DES is −
- Round function
- Key schedule
- Any additional processing − Initial and final permutation
Initial and Final Permutation
The initial and final permutations are straight Permutation boxes (P-boxes) that are inverses of each other. They have no cryptography significance in DES. The initial and final permutations are shown as follows −
Round Function
The heart of this cipher is the DES function, f. The DES function applies a 48-bit key to the rightmost 32 bits to produce a 32-bit output.
Expansion Permutation Box − Since right input is 32-bit and round key is a 48-bit, we first need to expand right input to 48 bits. Permutation logic is graphically depicted in the following illustration −
The graphically depicted permutation logic is generally described as table in DES specification illustrated as shown −
XOR (Whitener). − After the expansion permutation, DES does XOR operation on the expanded right section and the round key. The round key is used only in this operation.
Substitution Boxes. − The S-boxes carry out the real mixing (confusion). DES uses 8 S-boxes, each with a 6-bit input and a 4-bit output. Refer the following illustration −
The S-box rule is illustrated below −
There are a total of eight S-box tables. The output of all eight s-boxes is then combined in to 32 bit section.
Straight Permutation − The 32 bit output of S-boxes is then subjected to the straight permutation with rule shown in the following illustration:
Key Generation
The round-key generator creates sixteen 48-bit keys out of a 56-bit cipher key. The process of key generation is depicted in the following illustration −
The logic for Parity drop, shifting, and Compression P-box is given in the DES description.
DES Analysis
The DES satisfies both the desired properties of block cipher. These two properties make cipher very strong.
Generate a csr and private key. Avalanche effect − A small change in plaintext results in the very great change in the ciphertext.
Completeness − Each bit of ciphertext depends on many bits of plaintext.
During the last few years, cryptanalysis have found some weaknesses in DES when key selected are weak keys. These keys shall be avoided.
DES has proved to be a very well designed block cipher. There have been no significant cryptanalytic attacks on DES other than exhaustive key search.
∟Introduction to DES Algorithm
∟DES Key Schedule (Round Keys Generation) Algorithm
This section describes DES (Data Encryption Standard) algorithm - A 16-round Feistel cipher with block size of 64 bits.
Key schedule algorithm:
DES key schedule supporting tables:
Permuted Choice 1 - PC1:
Permuted Choice 2 - PC2:
Left shifts (number of bits to rotate) - r1, r2, ., r16:
Table of Contents
About This Book
Cryptography Terminology
Cryptography Basic Concepts
Des Key Generation 56 Bits 2
Introduction to AES (Advanced Encryption Standard)
►Introduction to DES Algorithm
What Is Block Cipher?
DES (Data Encryption Standard) Cipher Algorithm
►DES Key Schedule (Round Keys Generation) Algorithm
DES Decryption Algorithm
DES Algorithm - Illustrated with Java Programs
DES Algorithm Java Implementation
DES Algorithm - Java Implementation in JDK JCE
DES Encryption Operation Modes
DES in Stream Cipher Modes
PHP Implementation of DES - mcrypt
Blowfish - 8-Byte Block Cipher
Secret Key Generation and Management
Cipher - Secret Key Encryption and Decryption
Introduction of RSA Algorithm
RSA Implementation using java.math.BigInteger Class
Introduction of DSA (Digital Signature Algorithm)
Java Default Implementation of DSA
Private key and Public Key Pair Generation
PKCS#8/X.509 Private/Public Encoding Standards
Adobe ideas free download for android. Cipher - Public Key Encryption and Decryption
MD5 Mesasge Digest Algorithm
SHA1 Mesasge Digest Algorithm
OpenSSL Introduction and Installation
OpenSSL Generating and Managing RSA Keys
OpenSSL Managing Certificates
OpenSSL Generating and Signing CSR
OpenSSL Validating Certificate Path
'keytool' and 'keystore' from JDK
Key Generator
'OpenSSL' Signing CSR Generated by 'keytool'
Migrating Keys from 'keystore' to 'OpenSSL' Key Files
Certificate X.509 Standard and DER/PEM Formats
Migrating Keys from 'OpenSSL' Key Files to 'keystore'
Using Certificates in IE
Using Certificates in Google Chrome
Using Certificates in Firefox
Outdated Tutorials
References
Des Key Generation 56 Bits Download
Full Version in PDF/EPUB