Generate A Private Key From Csr
Generate a certificate signing request
Before you can install a Secure Socket Layer (SSL) certificate, you must first generate a certificate signing request (CSR). You can do this by using one of the following methods:
How to generate a CSR in Microsoft IIS 7. Click Start, then Administrative Tools, then Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager. Click on the server name. From the center menu, double-click the 'Server Certificates' button in the 'Security' section (it is near the bottom of the menu). Note: server.key and servercsr.txt are the Private key and the CSR code files. Feel free to use any file names, as long as you keep the.key and.txt extensions. Tip: if you want to generate the Private key and CSR code in another location from the get go, skip step 3.1. And replace the openssl part of the command with.OpenSSL base folder.
OpenSSL
The following sections describe how to use OpenSSL to generate a CSR for a single host name. If you want to generate a CSR for multiple host names, we recommend using the Cloud Control Panel or the MyRackspace Portal.
Before you can order an SSL certificate, it is recommended that you generate a Certificate Signing Request (CSR) from your server or device. Learn more about SSL certificates » A CSR is an encoded file that provides you with a standardized way to send DigiCert your public key as well as some. In order to prevent the situation when you loose your CSR code and Private Key, we automatically send the CSR code and the Private Key to the email which you provided when using the CSR Generator from above. Please check your email, so as we always send a message from SSL Dragon (email protected) where we include your CSR code and Private Key.
Install OpenSSL
Check whether OpenSSL is installed by using the following command:
CentOS® and Red Hat® Enterprise Linux®
The following output provides an example of what the command returns:
Debian® and the Ubuntu® operating system
The following output provides an example of what the command returns:
If the preceding packages are not returned, install OpenSSL by running the following command:
CentOS and Red Hat
Debian and the Ubuntu operating system
Generate the RSA key
Run the following commands to create a directory in which to store your RSA key, substituting a directory name of your choice:
Run the following command to generate a private key:
Create a CSR
Run the following command to create a CSR with the RSA private key (output is in Privacy-Enhanced Mail (PEM) format):
When prompted, enter the necessary information for creating a CSR by using the conventions shown in the following table.
Note: You cannot use the following characters in the Organization Name or Organizational Unit fields: < > ~ ! @ # $ % ^ * / ( ) ? . , &
| Field | Explanation | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Common Name | The fully qualified domain name to which the certificate applies. The domain names example.com and www.example.com are distinct from each other, so be sure to submit your request for the right domain. If you are purchasing a wildcard certificate, use *.example.com. | example.com |
| Organization Name | The exact legal name of your organization. The Certificate Authority (CA) might seek to confirm that your organization is real and legally registered, so don’t abbreviate words that aren’t abbreviated in the organization’s legal name. | Example Inc. |
| Organizational Unit | The branch of your organization that is making the request. | Marketing |
| City/locality | The city where your organization is legally located. Do not abbreviate the city name. | San Antonio |
| State/province | The state or province where your organization is legally located. Do not abbreviate the state or province name. | Texas |
| Country/region | The two-letter International Standards Organization (ISO) abbreviation for your country. | US |
Warning: Leave the challenge password blank (press Enter).
Verify your CSR
Run the following command to verify your CSR:
After you have verified your CSR, you can submit it to a CA to purchase an SSL certificate.
Windows IIS Manager
Use the following steps to generate a CSR by using Windows IIS Manager:
Note: The following steps are for IIS 8 or IIS 8.5 on Windows Server 2012.
- Open IIS Manager.
- In the left-hand Connections pane, click the server for which you want to generate a CSR.
- In the center server Home pane under the IIS section, double-click Server Certificates.
- In the right-hand Actions pane, click Create Certificate Request.
In the Request Certificate wizard, on the Distinguished Name Properties page, enter the following information and then click Next.
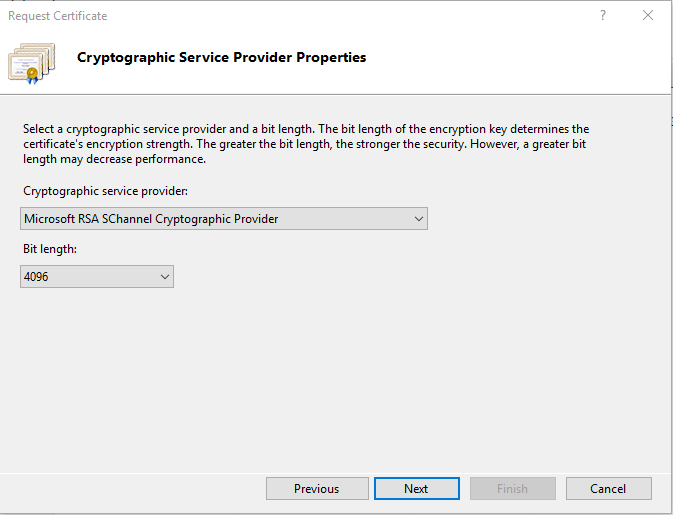
Field Explanation Example Common Name The fully qualified domain name to which the certificate applies. The domain names example.com and www.example.com are distinct from each other, so be sure to submit your request for the right domain. If you are purchasing a wildcard certificate, use *.example.com. example.com Organization Name The exact legal name of your organization. The CA might seek to confirm that your organization is real and legally registered, so don’t abbreviate words that aren’t abbreviated in the organization’s legal name. Example Inc. Organizational Unit The branch of your organization that is making the request. Marketing City/locality The city where your organization is legally located. Do not abbreviate the city name. San Antonio State/province The state or province where your organization is legally located. Do not abbreviate the state or province name. Texas Country/region The two-letter ISO abbreviation for your country. US On the Cryptographic Server Provider Properties page, enter the following information and then click Next.
- Cryptographic service provider: Unless you have a specific cryptographic provider, use the default selection.
- Bit length: 2048 is the recommended bit length.
- On the File Name page, enter the location where you want to save the certificate request file and then click Finish.
After you have generated the CSR, you can submit it to a CA to purchase an SSL certificate.
Cloud Control Panel
Rackspace provides the CSR Generator for generating a CSR. The CSR Generator shows you the CSRs that you currently have and lets you create new CSRs with a simple form. After you have entered your details, the generator combines them with your private key so that you can submit the combined encoded information to a CA.
When you are done with the generator, you can return to the Cloud Control Panel by clicking any of the links in the top navigation or by going to login.rackspace.com and selecting Rackspace Cloud from the drop-down product menu in the top navigation bar.
Access the CSR Generator
Access the CSR Generator directly or through the Control Panel by using the following steps:
- Log in to the Cloud Control Panel and select Rackspace Cloud from the drop-down product menu in the top navigation bar.
- In the top navigation bar, click Servers > Cloud Servers.
- Click the name of the server for which you want to generate a CSR.
- In the right-hand Managing Your Server section under Help me with, click Generate a CSR.
The generator lists your existing CSRs, if you have any, organized by domain name.
Generate a CSR
Click Create CSR.
Enter the following information, which will be associated with the CSR:
Field Explanation Example Domain Name The fully qualified domain name to which the certificate applies. The domain names example.com and www.example.com are distinct from each other, so be sure to submit your request for the right domain. If you want to secure both domains, you can use the Alt Names field. If you are purchasing a wildcard certificate, use *.example.com. example.com Alt Names (Optional) Additional domains that you want to add to the request. Each CA treats these differently, and the CA might charge for additional names. You can submit a comma-separated list. www.example.com, secure.example.com Email Address (Optional) A contact email address for the certificate. support@example.com Organization Name The exact legal name of your organization. The CA might seek to confirm that your organization is real and legally registered, so don’t abbreviate words that aren’t abbreviated in the organization’s legal name. Example Inc. Organizational Unit (Optional) The branch of your organization that is making the request. Marketing City The city where your organization is legally located. Do not abbreviate the city name. San Antonio State or Province The state or province where your organization is legally located. Do not abbreviate the state or province name. Texas Country Choose your country from the drop-down menu. The two-letter ISO abbreviation for your country is included in the CSR. United States Private Key Bit Length Key sizes smaller than 2048 are considered insecure and might not be accepted by a CA. 1024,2048,4096 Hashing Algorithm Both algorithms are currently trusted in mainstream browsers and offer industry recommended security. SHA-512 requires additional CPU processing. SHA-256, SHA-512 Note: You cannot use the following characters in the Organization Name or Organizational Unit fields:
< > ~ ! @ # $ % ^ * / ( ) ? . , &After you have entered all the required information, click Create CSR.
It can take between 5 and 60 seconds for the CSR to be generated. You might need to refresh the page that displays your CSRs before the new CSR is listed.
View CSR details
When CSR has been generated, you can click its UUID (unique identifier) in the CSR list to view its details screen.
This screen displays the information that you provided, the text of the CSR, and its associated private key.
Submit the CSR to the CA
The text in the Certificate Request field is the CSR. It contains encoded details of the CSR and your public key.
To request your SSL certificate, copy the Certificate Request text and submit it to your CA. Include all the text, including the BEGIN and END lines at the beginning and end of the text block.
Install the private key
Copy the private key to the server that will host the certificate. See your application documentation to determine where to install the private key and certificate on your server.
MyRackspace Portal
If you are a Managed or Dedicated customer, you can request a CSR through the MyRackspace Portal by using the following steps:
- Log in to the MyRackspace Portal and select Dedicated Hosting from the drop-down product menu in the top navigation bar.
- In the top navigation bar, click Tickets > Create Ticket.
- On the Tickets / Create New Ticket page, select Generate Certificate Signing Request (CSR) from the Subject drop-down list.
Enter the following information in the Ticket Details section:
Field Explanation Example Device(s) The server or servers for which you want to generate a CSR. Use the drop-down menu to select your servers. Common Name The fully qualified domain name to which the certificate applies. The domain names example.com and www.example.com are distinct from each other, so be sure to submit your request for the right domain. If you want to secure both domains, you can use the Alt Names field. If you are purchasing a wildcard certificate, use *.example.com. example.com Alt. Names (Optional) Additional domains that you want to add to the request. Each CA treats these differently, and the CA might charge for additional names. You can submit a comma-separated list. www.example.com, secure.example.com Email Address (Optional) A contact email address for the certificate. support@example.com Organization The exact legal name of your organization. The CA might seek to confirm that your organization is real and legally registered, so don’t abbreviate words that aren’t abbreviated in the organization’s legal name. Example Inc. Organizational Unit (Optional) The branch of your organization that is making the request. Marketing Locality (City) The city where your organization is legally located. Do not abbreviate the city name. San Antonio State or Province Name The state or province where your organization is legally located. Do not abbreviate the state or province name. Texas Country Choose your country from the drop-down menu. The two-letter ISO abbreviation for your country is included in the CSR. United States Note: The bit length is automatically set to 2048.
- Click Create Ticket.
Next steps
Reference
Experience what Rackspace has to offer.
©2020 Rackspace US, Inc.
Except where otherwise noted, content on this site is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License
Important: This example is intended to provide general guidance to IT professionals who are experienced with SSL requirements and configuration. The procedure described in this article is just one of many available methods you can use to generate the required files. The process described here should be treated as an example and not as a recommendation.
When you configure Tableau Server to use Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) encryption, this helps ensure that access to the server is secure and that data sent between Tableau Server and Tableau Desktop is protected.
Generate A Private Key From Csr Program
Looking for Tableau Server on Linux? See Example: SSL Certificate - Generate a Key and CSR.
Tableau Server uses Apache, which includes OpenSSL. You can use the OpenSSL toolkit to generate a key file and Certificate Signing Request (CSR) which can then be used to obtain a signed SSL certificate.
Steps to generate a key and CSR
To configure Tableau Server to use SSL, you must have an SSL certificate. To obtain the SSL certificate, complete the steps:
- Generate a key file.
- Create a Certificate Signing Request (CSR).
- Send the CSR to a certificate authority (CA) to obtain an SSL certificate.
- Use the key and certificate to configure Tableau Server to use SSL.
You can find additional information on the SSL FAQ page on the Apache Software Foundation website.
Configure a certificate for multiple domain names
Tableau Server allows SSL for multiple domains. To set up this environment, you need to modify the OpenSSL configuration file, openssl.conf, and configure a Subject Alternative Name (SAN) certificate on Tableau Server. See For SAN certificates: modify the OpenSSL configuration file below.
Set the OpenSSL configuration environment variable (optional)
To avoid using the -config argument with every use of openssl.exe, you can use the OPENSSL_CONF environment variable to ensure that the correct configuration file is used and all configuration changes made in subsequent procedures in this article produce expected results (for example, you must set the environment variable to add a SAN to your certificate).
Open the Command Prompt as an administrator, and run the following command:
set OPENSSL_CONF=c:Program FilesTableauTableau Serverpackagesapache.<version_code>confopenssl.cnf
Notes:
When setting the Open SSL configuration environment variable, do not enclose the file path with quotation marks.
If you are using a 32-bit version of Tableau Server on a 64-bit computer, run the
set OPENSSL_CONF=c:Program Files (x86)TableauTableau Serverpackagesapache.<version_code>confopenssl.cnfcommand instead.
Generate a key
Generate a key file that you will use to generate a certificate signing request.
Open the Command Prompt as an administrator, and navigate to the Apache directory for Tableau Server. For example, run the following command:
cd C:Program FilesTableauTableau Serverpackagesapache.<version_code>binRun the following command to create the key file:
openssl.exe genrsa -out <yourcertname>.key 4096Note: This command uses a 4096-bit length for the key. You should choose a bit length that is at least 2048 bits because communication encrypted with a shorter bit length is less secure. If a value is not provided, 512 bits is used.
Create a certificate signing request to send to a certificate authority
Use the key file you created in the procedure above to generate the certificate signing request (CSR). You send the CSR to a certificate authority (CA) to obtain a signed certificate.
Important: If you want to configure a SAN certificate to use SSL for multiple domains, first complete the steps in For SAN certificates: modify the OpenSSL configuration file below, and then return to here to generate a CSR.
Run the following command to create a certificate signing request (CSR) file:
openssl.exe req -new -key yourcertname.key -out yourcertname.csrIf you did not set the OpenSSL configuration environment variable,
OPENSSL_CONF, you might see either of the following messages:An error message about the config information being unable to load. In this case, retype the command above with the following parameter:
-config .confopenssl.cnf.A warning that the
/usr/local/ssldirectory cannot be found. This directory does not exist on Windows, and you can simply ignore this message. The file is created successfully.
To set an OpenSSL configuration environment variable, see Set the OpenSSL configuration environment variable (optional) section in this article.
When prompted, enter the required information.
Note: For Common Name, type the Tableau Server name. The Tableau Server name is the URL that will be used to reach the Tableau Server. For example, if you reach Tableau Server by typing
tableau.example.comin the address bar of your browser, thentableau.example.comis the common name. If the common name does not resolve to the server name, errors will occur when a browser or Tableau Desktop tries to connect to Tableau Server.
Openssl Generate Key From Csr
Send the CSR to a certificate authority to obtain an SSL certificate
Send the CSR to a commercial certificate authority (CA) to request the digital certificate. For information, see the Wikipedia article Certificate authority and any related articles that help you decide which CA to use.
Use the key and certificate to configure Tableau Server
When you have both the key and the certificate from the CA, you can configure Tableau Server to use SSL. For the steps, see Configure External SSL.
For SAN certificates: modify the OpenSSL configuration file
In a standard installation of OpenSSL, some features are not enabled by default. To use SSL with multiple domain names, before you generate the CSR, complete these steps to modify the openssl.cnf file.
Open Windows Explorer and browse to the Apache conf folder for Tableau Server.
For example:
C:Program FilesTableauTableau Server<version_code>apacheconfZoom h4n driver mac download. Open openssl.cnf in a text editor, and find the following line:
req_extensions = v3_reqThis line might be commented out with a hash sign (#) at the beginning of the line.
If the line is commented out, uncomment it by removing the # and space characters from the beginning of the line.
Move to the [ v3_req ] section of the file. The first few lines contain the following text:
# Extensions to add to a certificate request
basicConstraints = CA:FALSE
keyUsage = nonRepudiation, digitalSignature, keyEnciphermentAfter the keyUsage line, insert the following line:
subjectAltName = @alt_namesIf you’re creating a self-signed SAN certificate, do the following to give the certificate permission to sign the certificate:
Add the
cRLSignandkeyCertSignto the keyUsage line so it looks like the following:keyUsage = nonRepudiation, digitalSignature, keyEncipherment, cRLSign, keyCertSignAfter the keyUsage line, add the following line:
subjectAltName = @alt_names
In the [alt_names] section, provide the domain names you want to use with SSL.
DNS.1 = [domain1]
DNS.2 = [domain2]
DNS.3 = [etc]The following image shows the results highlighted, with placeholder text that you would replace with your domain names.
Save and close the file.
Complete the steps in Create a certificate signing request to send to a certificate authority section, above.
Additional information
If you prefer to use a different version of OpenSSL, you can download it from Open SSL for Windows.